Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2026-01-13 Origin: Site
Are you wondering if LASER WELDING MACHINES always need gas for welding? The role of shielding gas in laser welding is often debated, with some thinking it’s optional. However, gas plays a crucial role in preventing defects like oxidation and ensuring strong, clean welds.
In this article, we’ll explore why shielding gas is commonly required in laser welding and when it may not be necessary. You’ll learn the types of gases used and how they contribute to weld quality and machine longevity.
During laser welding, the molten metal is highly reactive and can easily oxidize when exposed to oxygen and nitrogen in the air. This can lead to defects such as brittleness and porosity. Shielding gas forms a protective barrier around the weld pool, preventing atmospheric contamination and ensuring the weld remains clean and strong.
The use of shielding gas is particularly important when welding reactive metals like stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium. These metals are highly sensitive to oxidation, and without gas, the weld may be compromised, leading to poor mechanical properties and a weak joint. The oxidation can also cause discoloration, which is often unacceptable in industries where aesthetic quality is important, such as in the production of electronics or medical devices.
Tip: For metals like aluminum and titanium, which are prone to oxidation, always ensure the use of suitable shielding gas to maintain weld strength and integrity.
At high power levels, the interaction between the laser beam and the material can create a plasma cloud. This cloud absorbs and scatters the laser energy, reducing its effectiveness and making it harder to achieve deep penetration. Shielding gases, especially those with high ionization potential like helium, help suppress plasma formation, ensuring that the laser energy is fully utilized for welding the material.
In high-power applications, the plasma cloud can become so dense that it prevents the laser beam from reaching the material. This results in poor weld quality and can lead to under-penetration or inconsistent fusion. Shielding gas like helium or helium-rich mixtures significantly reduce plasma density, making the welding process more efficient and improving the overall quality of the weld.
The optics of a LASER WELDING MACHINE are vital for focusing the laser beam onto the workpiece. During welding, metal vapor, smoke, and spatter can damage the lens or other optical components. Shielding gas helps keep the optics clean by preventing the buildup of debris on the lens. Without this protection, operators may experience frequent lens failures, which can be costly and affect production.
The optics are critical to maintaining the focus and accuracy of the laser beam. Without proper shielding gas, the buildup of metal vapor and spatter on the lens could lead to misalignment of the beam, potentially causing defects in the weld and making it impossible to perform precise welding. This could result in higher downtime and maintenance costs, as well as delays in production.
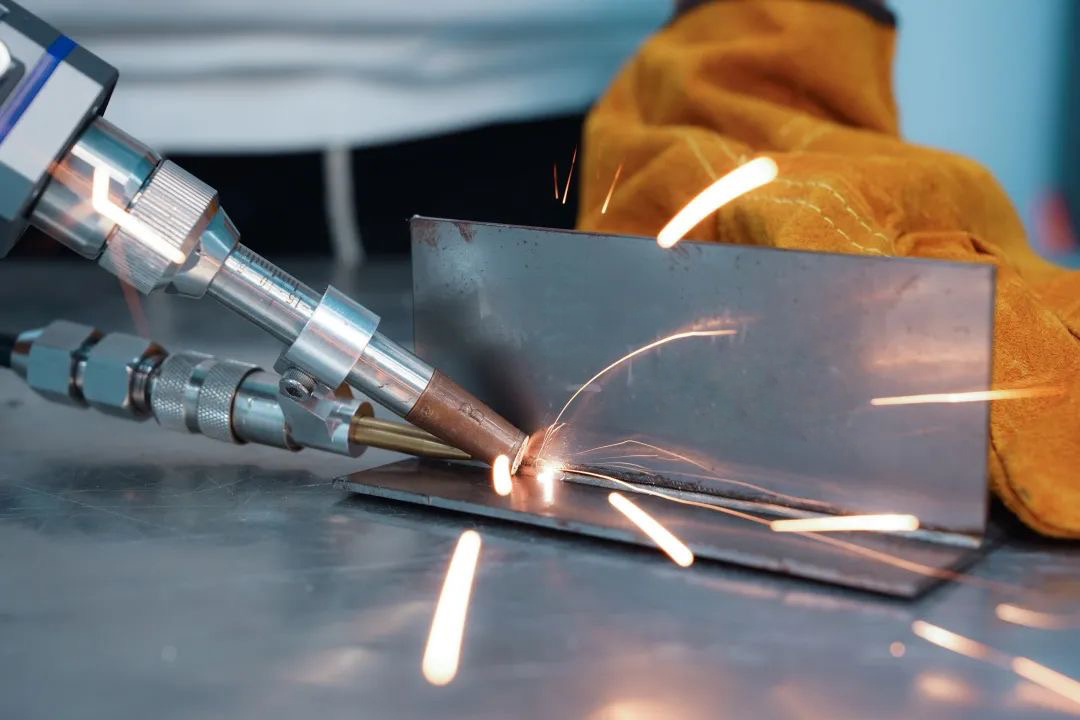
In certain non-critical applications, where minor defects or surface oxidation are acceptable, gas may not be necessary. For example, temporary welds or cosmetic welds on non-structural components can often be done without shielding gas. Additionally, low-power laser welding, where the energy interaction is minimal, may not generate enough plasma to require shielding gas.
For low-power laser welding, especially on materials like carbon steel, the welding process may not produce sufficient plasma formation to warrant the use of gas. In these cases, operators may decide to skip the gas to reduce costs. However, it is important to note that even in these scenarios, the weld quality might be compromised, and surface oxidation could still occur, affecting the long-term durability of the weld.
Tip: For temporary applications or welding non-critical components, skipping gas might be acceptable. However, always weigh the risk of reduced weld quality and potential long-term issues.
In some cases, welding is performed in controlled environments, such as vacuum chambers or inert atmospheres. These settings can eliminate the need for additional shielding gas, as the atmosphere is already inert or controlled. For example, welding in a vacuum can prevent oxidation without the need for a separate gas supply.
Similarly, in industries like semiconductor manufacturing, where cleanroom environments are used, the controlled air supply may already provide a sufficient barrier to oxidation. In such controlled conditions, using additional shielding gas is often unnecessary and could even be counterproductive, as it may alter the environment in undesirable ways.
Some non-reactive metals, like carbon steel, may not require shielding gas, especially under low-power settings or if oxidation is not a concern. In these cases, gases like compressed air or even no gas may be sufficient for achieving an acceptable weld. However, for thicker materials or high-power welding, gas is typically necessary to prevent defects.
Carbon steel is less prone to oxidation than metals like stainless steel, so in low-power applications or situations where surface oxidation is acceptable, gas might not be required. This can help save on costs, especially in large-scale production environments where welding costs are a significant factor.
Different types of gases are used depending on the material being welded and the desired weld quality. The choice of gas significantly affects the weld penetration, appearance, and overall quality. Below are some common gases used in laser welding:
Argon is one of the most commonly used shielding gases in laser welding. It is an inert gas, meaning it does not react with the molten weld pool, providing excellent protection against oxidation. Argon is ideal for welding non-ferrous metals, such as aluminum and stainless steel, as it prevents the formation of oxides and ensures a clean, strong weld.
Gas | Main Uses | Advantages |
Argon | Aluminum, stainless steel, titanium | Cost-effective, stable, excellent oxidation protection |
Helium is used in laser welding for its high thermal conductivity, which helps to transfer heat more efficiently. It is especially beneficial for welding thick or reflective materials, such as copper and brass, as it provides deeper penetration and faster welding speeds. Helium also helps to suppress plasma formation during high-power laser welding.
Gas | Main Uses | Advantages |
Helium | Copper, brass, thick materials | Provides deep penetration, reduces plasma formation |
Nitrogen is often used in laser welding, particularly for stainless steel and other alloys. It enhances weld penetration and can improve the mechanical properties of the weld. However, nitrogen can react with certain metals to form nitrides, so it’s important to use it carefully.
Gas | Main Uses | Advantages |
Nitrogen | Stainless steel, certain alloys | Cost-effective, enhances penetration, improves strength |
In some cases, a combination of gases is used to optimize the welding process. For example, a helium-argon mixture is often used to balance heat transfer and oxidation resistance. These mixtures are custom-designed for specific applications to achieve the best weld quality.
Gas Mixture | Main Uses | Advantages |
Argon-Helium | Aluminum, copper, thick materials | Balances heat input, reduces spatter, enhances penetration |
One of the primary risks of skipping shielding gas is the potential for lens destruction. During the welding process, metal vapor and spatter can be released, which, without a gas shield, can coat the laser lens. This can cause the lens to overheat, crack, and become damaged, resulting in costly repairs and downtime.
Without gas, stainless steel and other reactive metals are susceptible to oxidation, which leads to the formation of “sugaring”—a black oxide layer on the back of the weld. This compromises the metal’s integrity and aesthetic appearance. Without proper shielding, the welding process itself can be severely compromised.
The absence of gas also compromises the cooling system of the laser welding machine. Shielding gas helps cool the copper nozzle and tip, and without it, the reflected laser energy can cause these components to overheat. This could result in deformation or even complete failure of the components, leading to more costly repairs.
In conclusion, LASER WELDING MACHINES generally require shielding gas for optimal results. Gas plays a critical role in protecting the weld pool from oxidation, stabilizing the laser beam, and preventing damage to the machine’s optics. While some applications may not require gas, especially for low-power or non-critical welding, using the appropriate shielding gas ensures cleaner, stronger, and more reliable welds.
Nanjing Speedy Laser Technology Co., Ltd. offers high-quality LASER WELDING MACHINES designed to meet various welding needs. Their products provide precise and efficient solutions for industries that require top-notch performance and durability in their welding processes.
A: Most of the time, LASER WELDING MACHINES require shielding gas to protect the molten metal and prevent defects like oxidation and porosity. However, in some low-power or non-critical applications, gas may not be necessary.
A: Shielding gas protects the weld pool from contamination by atmospheric gases. It also stabilizes the laser beam and prevents damage to the optics, ensuring high-quality welds without defects.
A: Yes, in specific cases such as welding non-reactive metals like carbon steel, or in controlled environments, gas can sometimes be omitted. However, skipping gas is not recommended for high-power or precision welding.
A: Common gases include argon, helium, and nitrogen. Argon is widely used for its stability, while helium provides better heat transfer. Nitrogen is often used for welding stainless steel.
A: Without shielding gas, the weld pool can be contaminated by oxygen, leading to oxidation and poor weld quality. Additionally, the optics of the LASER WELDING MACHINE can be damaged by spatter and smoke, reducing its effectiveness.